Method for identification of textile fabrics
Textile fabric identification can mainly start from three latitudes, the composition of textile fabric, the positive and negative sides of textile fabric, the warp and weft direction, and the appearance quality of textile fabric. Through the identification of these three directions, it can help fabric buyers to find good fabrics with good quality and low price. Below, Xiaobian detailed introduction of the three categories of identification of specific methods, learn to oh ~

Identification of textile fabric components
1. Sensory discrimination
(1) Main methods
Eye: use the visual effect of the eye to observe the luster and shade of the fabric, the dyeing condition, whether the surface is rough or not, and the appearance characteristics of the tissue, grain and fiber.
Hand touch: use the touch effect of the hand to feel the soft and hard, smooth, rough, fine and clean, elastic, cold and warm, etc. You can also feel the strength and elasticity of the fibers and yarns in the fabric by hand.
Ear hearing, nose smell: hearing and smell to judge the raw material of certain fabrics have certain help. Such as silk has a unique sound; Different kinds of different fiber fabric tearing sound is different; The odor of acrylic fiber and wool fiber fabric is different.
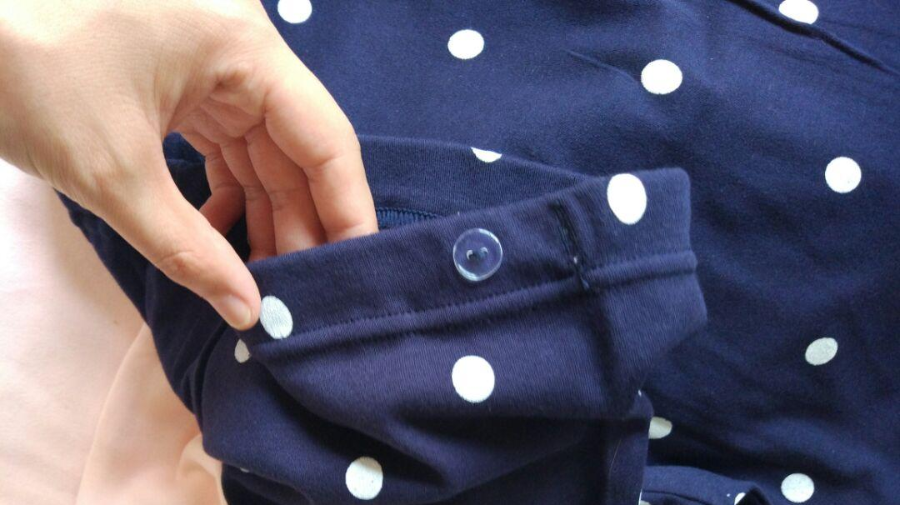

(2) Four steps
Above all, what distinguish fiber or fabric preliminarily belongs to big class.
The second step is to further determine the type of raw materials by the sensory characteristics of the fibers in the fabric.
The third step is to make a final judgment based on the sensory characteristics of the fabric.
The fourth step is to verify the judgment results. If the judgment is uncertain, other methods can be used to verify. If the judgment is wrong, sensory identification can be carried out again or combined with other methods for identification.
2. Combustion identification
Combustion characteristics of common textile fibers
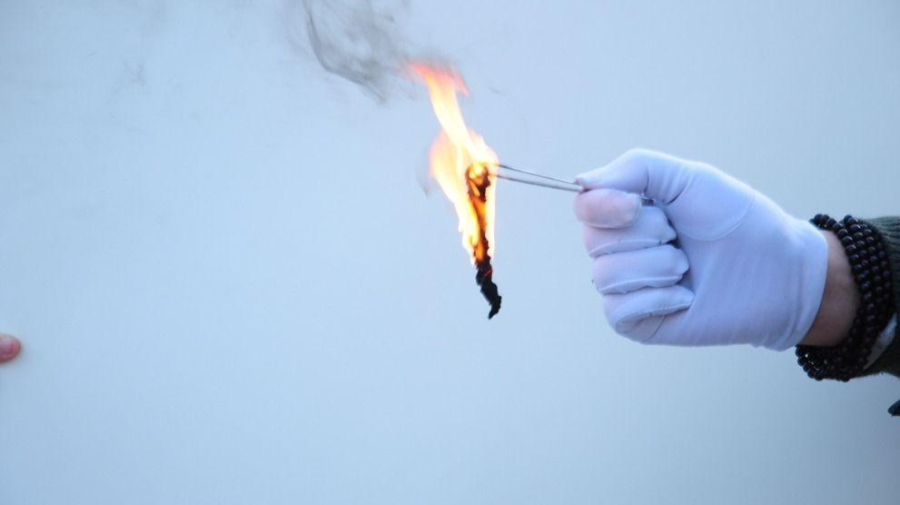

(1) Cotton fiber, in case of fire is burning, burning speed is fast, produce yellow flame, smell; Slight gray smoke, from the fire can continue to burn, after blowing out the flame there are still sparks in the continued burning, but the duration is not long; After burning, it can keep the shape of velvet, and it is easily broken into loose ash when touched by hand. The ash is gray fine soft powder, and the burnt part of the fiber is black.
② Hemp fiber, burning fast, softening, not melting, not shrinking, producing yellow or blue flame, there is the smell of burning grass; To continue burning rapidly away from the flame; Ashes less, light gray or white grass ash shape.
(3) wool, contact with the flame does not immediately burn, first rolled up, after smoke, and then the fiber started burning; The flame is orange yellow, burning speed is slower than cotton fiber, leaving the flame immediately stop burning, not easy to continue burning, there is a smell of burning hair and feathers; Ash can not maintain the original state of the fiber, and amorphous or globular glossy black brown crisp block, with a finger that crush, the number of ash is more, there is the smell of combustion.
(4) silk, burning slowly, melt and curl, burning into a mass, there is the smell of singed hair; Leaving the flame with a little flash, slowly burning, sometimes self-extinguishing; Gray is black brown crisp ball, with a finger to crush.
⑤ viscose fiber, combustion characteristics are basically similar to cotton, but viscose fiber combustion speed is slightly faster than cotton fiber, less ashes, sometimes not easy to maintain the original shape, viscose fiber combustion will issue a slight hissing sound.
⑥ Acetate fiber, burning fast, spark, melting, burning, burning when the pungent acetic acid taste; Leaving the flame, while melting, while burning; Grey is black shiny irregular lumps, which can be crushed by fingers.
⑦ Copper ammonia fiber, burning fast, no melting, no contraction, there is the smell of burning paper; To continue burning rapidly away from the flame; Ashes less, light gray or grayish white.
⑧ nylon, close to the flame caused by the fiber contraction, contact with the flame, the fiber quickly rolled up, and melted into a transparent gel, while there are small bubbles.
⑨ Acrylic fiber, while melting, while burning, burning speed is fast; The flame is white, bright and powerful, sometimes a little black smoke; Having a fishy or pungent smell similar to that of burning coal tar; Continue to burn away from the flame, but at a slow rate; Ash for black brown irregular brittle ball, easy to break with fingers.
Attensible vinylon, when burning, the fibers shrink rapidly and burn slowly. The flame is small and almost smokeless. When a large amount of fiber melting will produce a large deep yellow flame, with small bubbles; Burned with a special stench of calcium gas; To continue to burn from the flame, and sometimes to die; Embers for black brown irregular brittle beads, fingers can be broken.
⑪ polypropylene, curled, and melt, slow combustion; There were bright blue flames, black smoke, and drips of jelly; The smell of burning paraffin wax; To continue to burn from the flame, and sometimes to die; Ashes are irregular hard blocks, transparent, not easy to break with fingers.
12) Bert, refractory to flammability; Melting in the flame, burning, emitting black smoke; If you leave the flame, it will be extinguished immediately. The pungent stench of chlorine is unpleasant when burned; Ashes for irregular black brown hard pieces, not easy to break with fingers.
In passing, the spandex, close to the flame, expands into a circle, then shrinks and melts; Melting combustion in the flame, the burning speed is relatively slow, the flame is yellow or blue; Leave the flame edge melting edge combustion, slow self-extinction; It has a special pungent smell when burned. The ash is a white, sticky mass.
3. Density gradient
The identification process of density gradient method is as follows: First configuration fluid density gradient, configuration method is two different density and mutual combination of light and heavy liquid appropriate mix, generally using xylene as light liquid, carbon tetrachloride as heavy liquid, using diffusion effect, the two kinds of liquid liquid interface light and heavy liquid molecules diffusion to each other, make the mixture density gradient in the tube forming a kind of continuous variation from top and bottom of density gradient liquid. Use balls of standard density to mark the density values at various heights. Then the textile fiber to be tested for deoiling, drying and other pretreatment, into the ball, the ball in turn into the density gradient tube, determination of the fiber density value, and the standard density of the fiber to do a comparison, so as to identify the type of fiber. Because the density gradient fluid changes with temperature, it is important to keep the temperature of the density gradient fluid constant when testing.
4. Microscopic observation
By observing the longitudinal morphology of textile fibers under a microscope, we can distinguish their categories. The specific name of the textile fiber can be determined by observing the cross-section shape of the fiber.

5. Dissolution method

For pure yarn fabric, identification, to a certain concentration of chemical reagent to have to identify the test tube of textile fiber, and then observe and carefully distinguish between dissolution of textile fibers (dissolved, dissolve, slightly soluble and insoluble), and carefully record the dissolving temperature (dissolve under normal temperature, heating, dissolving, boil to dissolve).
For blended fabrics, identification, the need to first split the fabric into a root of textile fiber, and then put the textile fiber on the concave slide, the fiber will be expanded, drop into the chemical reagent, under the microscope for observation, from the observation of component fiber dissolution, determine the type of fiber.
Since the concentration and temperature of chemical solvents have an obvious effect on the solubility of textile fibers, the concentration and temperature of chemical reagents should be strictly controlled when textile fibers are identified by solubility method.
6. Reagent coloring method
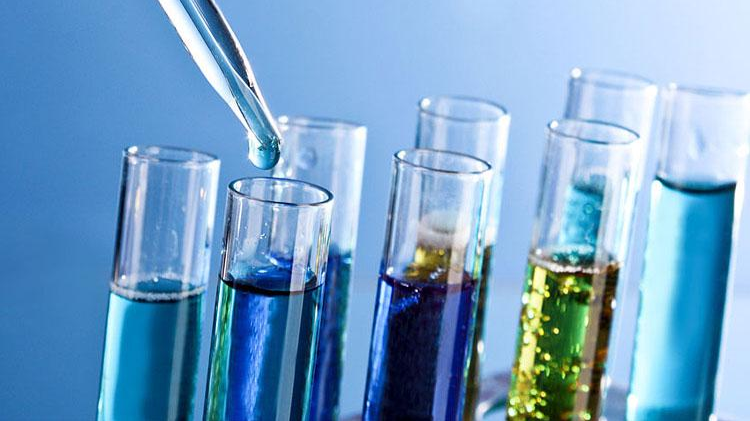

Reagent coloring method is a rapid method to identify textile fiber varieties according to the different coloring properties of various textile fibers to certain chemical reagents. The reagent coloring method is only applicable to undyed or pure spun yarns and fabrics. For colored textile fibers or textile fabrics must be advanced decolorization.
7. Melting point method
Melting point method According to the different melting characteristics of various synthetic fibers, the melting point is measured by a melting point meter, so as to identify the varieties of textile fibers. Most synthetic fibers do not have an exact melting point, and the melting point of the same kind of synthetic fiber is not a fixed value, but the melting point is basically fixed in a relatively narrow range, so the type of synthetic fiber can be determined according to the melting point. This is one of the methods to identify synthetic fiber, this method is generally not only used, but after the initial identification as an auxiliary method of confirmation, only applicable to the pure spun synthetic fiber fabric without anti-melting treatment.
Recognition of front and back and warp and weft direction of textile fabric
1. Identification of the positive and negative sides of textile fabrics
Can be roughly divided into according to the organizational structure of the textile material identification (plain, twill and satin), according to the appearance of the textile fabric effect recognition (print, gauze fabric, towel fabric), according to the pattern recognition of textile fabrics, according to the characters of textile fabric cloth edge recognition, according to the appearance of the textile fabric specially after finishing effect recognition (terry fabrics, double layers of fabric, Burnt-out fabric), identified according to the trademark and seal of textile fabric, and identified according to the packaging form of textile fabric;
2. Identification of the warp and weft direction of textile fabrics
It can be identified from the fabric edge of the textile fabric, the density of the textile fabric, the raw material of the yarn, the twist of the yarn, the structure of the yarn, the size of the yarn, the reed identification, the density of the warp and weft yarn, the twist and the twist of the fabric, and the scalability of the fabric.
Identification of appearance quality of textile fabrics
1. Identification of textile fabric defects
The defects of textile fabrics include broken warp, sunken yarn, leaping, flanging, cobweb, holes, roving, slubby yarn, overbelly yarn, double weft, tight twist yarn, uneven sliver, thin weft, thin segment, dense path, Thick section, edge defects, neps, impurities, stains, color bars, rail, weft, hundreds of feet, crease, rolling spindle, SAO damage, wrong weft, loose warp, reed and reed wear fault, narrow fabric, twill reverse inconsistent, decorative pattern, color, decorative pattern, color, stripe, stripe is inconsistent, depth clip figure, skew, partial, desizing, color flower printing, with these defects, according to the appearance characteristics can be identified.
2. Identification of deteriorated textile fabrics
The main methods are seeing, touching, listening, smelling and licking.
Look, observe the color and lustre of fabrics, appearance, without the traces left by deterioration. Such as wind stains, oil stains, water spots, mildew spots, staining, discoloration or fabric normal and different characteristics.
Touch, hold the fabric with your hand, and feel if there are any symptoms of deterioration such as stiffness, moisture, sticky, fever, etc.
Listen, the sound produced by tearing the fabric and the normal fabric produced by the crisp sound contrast, such as voice dumb, turbid, silent, may occur deterioration.
Smell, through the smell of the fabric, to judge whether the fabric deterioration. In addition to the fabric after special finishing (such as coated with rainproof agent or resin treatment, etc.), any strange smell, such as acid, mildew, bleach smell, etc., indicates that the fabric has deteriorated.
Licking, after licking the fabric through the tongue, if there is flour moldy or sour taste, it means moldy.
Learn these methods, you are not a fabric novice, identify the fabric that is a matter of minutes.
Tel:0311-87877888 / 0311-87035555 / 13831145889 / 15831121695
Fax: 0311-87810345 Email:duwei@boshitex.com
Add:2309 Shangde Plaza, No. 8 Kangle Street, Xinhua District,Shijiazhuang City, Hebei China
Technical Support:ronglida.net.cn ICP15019912-2